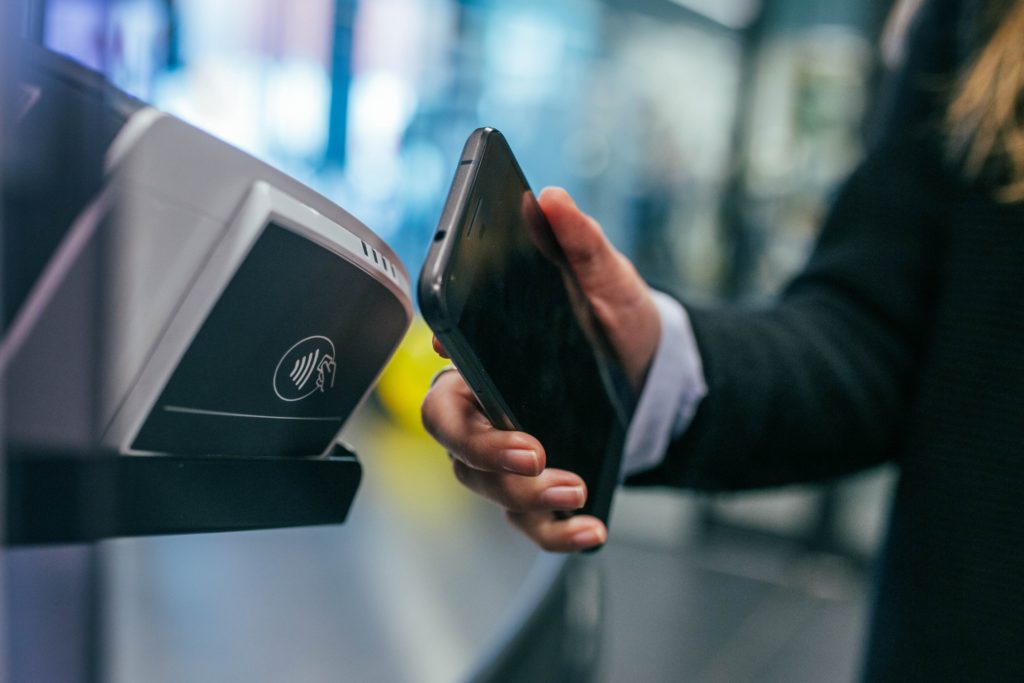
Have you ever experienced the irritating feeling when you have to queue up for 30 mins – 40 mins to be checked out? This scene can be easily witnessed if you go to the supermarket at the weekends or simply experience them if you join in the force accumulating products in panic under COVID-19 affection. I actually love shopping a lot, especially going around the supermarket, choose suitable items, weight up the different options then maybe finally decide to buy a few ones after considering the prices of all similar products. But the tedious process deters me from going to the supermarket. So how can we – retailers do about this? How does RFID help speed up store checkout with the stockpiled up to 1m within 1s? How can RFID be applied in different industries? You can check the answers below.
1. What exactly does RFID mean?
RFID stands for Radio Frequent Identification. It uses radio waves to read and capture information stored on a tag attached to an object, providing a unique identifier for an object. RFID Technology is used in many industries and in a wide variety of applications as it can deliver a number of benefits for organizations.

So if you imagine the functions of RFID, it might be similar to Barcode but it overweight Barcode in regards to functions: a wider range(using a wireless network) , keep richer data and reading products without the need for a line of sight and even more accurate.
Therefore, with the wide range of wireless network, RFID helps to read all products in one cart with “1 beep in 1 s”. Interesting, right?
That’s the reason you see customers easily leave the store without caring about checking out products. Shoplifting can be prevented as well, who can avoid the scanning of radiofrequency unless these people used a higher technology?
Recently a new benefit of RFID became obvious, through omnichannel sales RFID is able to increase customer satisfaction and move customers along the purchase path.
2. How does RFID work?
RFID belongs to a group of technologies referred to as Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC). AIDC methods automatically identify objects, collect data about them, and enter those data directly into computer systems with little or no human intervention. RFID methods utilize radio waves to accomplish this. At a simple level, RFID systems consist of three components: an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which are used to transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator). The reader then converts the radio waves to a more usable form of data. Information collected from the tags is then transferred through a communications interface to a host computer system, where the data can be stored in a database and analyzed at a later time.
3. How can RFID be applied in different industries?
With the above process, you might easily understand the first function is to checking out for customers that can be expanded as easily read/count the products so you can use them in the process in warehouse operation: count the products, receive products.
Besides, it can keep information of location so it assist the processes in picking up products to fulfill orders (which is used by Amazon in their very large warehouses).

The capability of RFID in keeping different kinds of data also helps to track down a lot of information and industries. The market for counterfeit goods in the United States exceeds $1 trillion annually, based on the value of goods seized by law enforcement
Using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) ensures product authenticity — individual items can be uniquely identified by serial numbers with EPC-enabled RFID, rather than just at the SKU level. Through more efficient authentication processes and the ability of RFID tags to hold more information about where the product was manufactured, the use of RFID in retail can significantly reduce the number of imitation products on the market.
You might not know that RFID is applied in Railway as well: The train needs to stop at a few determined points on their railway. RFID helps the train to stop accurately over the optical sensors which can fail due to debris.
4. Focusing on Retail Operation
Alright, let’s focus on Retail Operation. What is the benefit of RFID? We recommend you go further with the research: RFID Implementation in Retail Industry: Current Status, Issues, and Challenges by Bhattacharya, Mithu; Chu Chao-Hsien; Mullen Tracy (2007), from Decision Science Institute (DSI) Conference, Phoenix Arizona AZ, 2007, (pp 9-11).
Now, you can look at RFID by another view – the circle of supply chain with the appliance of RFID
5. If it’s too good, why do all retailers replace barcodes with RFID?

The benefit of RFID is irrefutable so this’s a good question and I think you can guess the answer. The fee of acquiring RFID technology is high than it is for using Barcode. Therefore, you have to consider other factors to see it it’s worth investing in RFID.
Just imagine, with the Barcode, you just print them on paper and label them on Products. With RFID, you have to acquire smart tags, RFID readers and a system which can be connected to RFID readers. Therefore, you need to consider ROI with all factors when consider to apply RFID.